“`html
Best 5 Solutions for Protecting Coral Reefs in 2025 – Discover How to Help
Coral reefs are among the most biodiverse ecosystems on our planet, playing a crucial role in supporting marine life and maintaining ocean health. Unfortunately, they are under severe threat due to climate change, ocean acidification, and human activities. This guide outlines five effective solutions to protect coral reefs by 2025, delving into practical actions we can take to ensure a thriving underwater habitat for generations to come.
1. Strengthening Marine Protected Areas
One of the most effective methods of safeguarding coral reefs is through establishing and strengthening marine protected areas (MPAs). These regions are designated to conserve marine ecosystems, providing a refuge for marine life and enhancing coral health. MPAs can help mitigate the impacts of fishing and pollution, allowing coral species to thrive. Countries around the world are recognizing the significance of these areas, with plans to increase their size and number. Ensuring strict regulations within MPAs is crucial for reducing stressors on vulnerable ecosystems and providing coastal protection.
Effective Management Strategies
To ensure successful implementation, effective management strategies must be in place for these protected areas. Involving local communities in the decision-making process fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards reefs conservation. Strategies may include regular monitoring of fish populations and coral health, addressing illegal fishing practices, and promoting sustainable tourism in partnership with local enterprises. With the community’s involvement and support, MPAs can become vibrant ecosystems that enhance local biodiversity and sustain reef ecosystems.
Benefits to Marine Biodiversity
MPAs not only provide a safe haven for sensitive species but also contribute to the overall resilience of the ocean’s biodiversity hotspots. By maintaining ecological balance, MPAs promote essential processes such as coral spawning, which participants of marine biology research can study to gain a better understanding of coral ecology and reef dynamics. Increased fish stocks can also boost local fisheries, benefiting the economy while supporting the regeneration of coral habitats.
2. Enhancing Coral Restoration Practices
Coral restoration is crucial for reviving degraded areas of reef ecosystems. Innovative techniques, such as coral propagation and coral gardening, significantly aid in regeneration of corals. By growing coral species in nurseries and subsequently transplanting them into depleted areas, marine conservationists are witnessing the successful recovery of reefs. Community members can engage in coral propagation techniques, actively contributing to restoring our ocean’s coral diversity.
Successful Case Studies of Coral Restoration
Various projects worldwide showcase the ability of restorative practices to enhance underwater habitats. For example, the Coral Triangle initiative has made significant strides in restoring coral reefs through targeted planting of native corals in degraded areas. These initiatives not only increase coral coverage but also improve overall fish populations, contributing to the ecosystem’s health. Local divers and conservationists can also create awareness around these restoration efforts through eco-tourism, encouraging sustainable practices.
Monitoring Coral Health and Resilience
Effective monitoring of coral health following restoration efforts is vital for understanding long-term success. Tools such as reef surveys and reef monitoring technologies, including underwater drones and remote sensing, can provide valuable data over time. This information helps conservationists pinpoint areas for improvement and determine how climate change impacts coral resilience, offering a clearer path for future interventions.
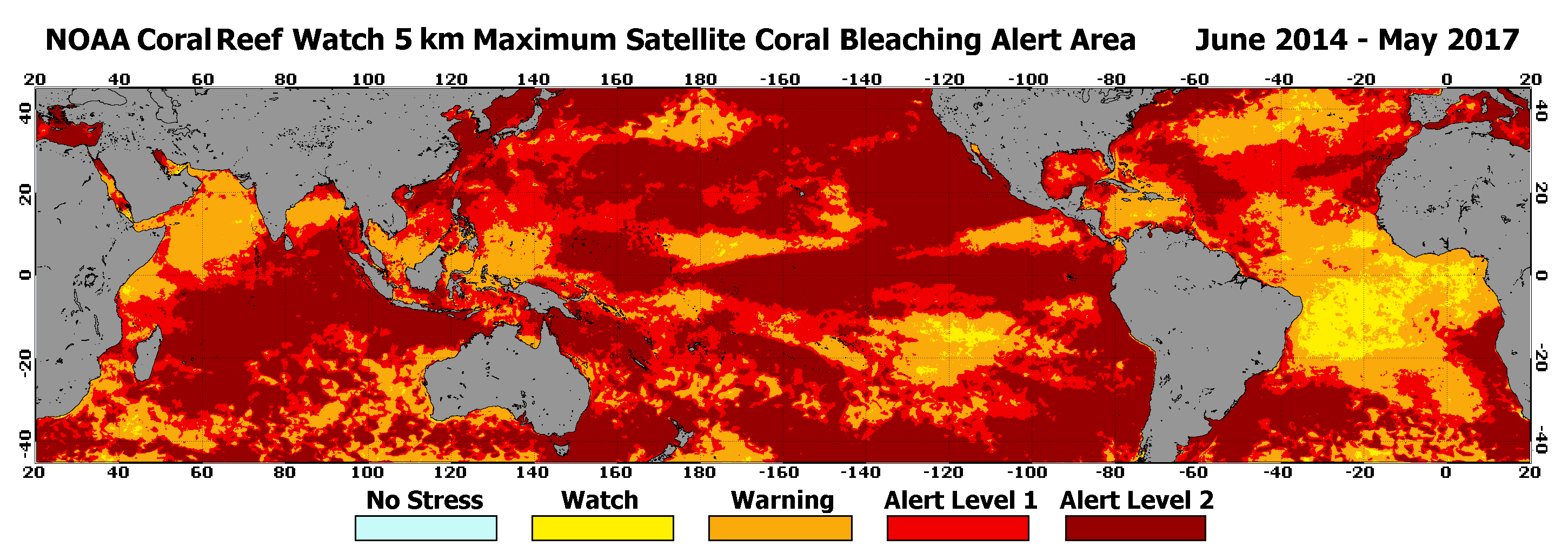
3. Combating Coral Bleaching through Climate Action
Coral bleaching poses one of the greatest threats to coral reefs worldwide, driven primarily by rising ocean temperatures as a result of climate change. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is essential to slow the pace of climate change. Globally, efforts are underway to meet or exceed commitments outlined in international agreements like the Paris Accord to limit global warming. Supporting clean energy initiatives and local policies aimed at mitigating climate change are steps individuals and communities can take to drive change and protect corals.
Advocacy and Education on Climate Change Impacts
Raising awareness about the impacts of climate change on coral reefs is essential in fostering public engagement. Educational programs and initiatives focused on coral reef education can highlight how climate shifts affect coral symbiosis, causing stress and eventual bleaching. By empowering individuals to advocate for environmental protection, we can mobilize communities to engage in actions that promote overall carbon neutrality.
Collaborating Globally for Impact
Global collaboration among nations for marine conservation helps in aligning efforts against climate change and creating a more robust response to threats facing coral reefs. Initiatives like the Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network provide frameworks for cooperative research and action in coral protection. Advocacy initiatives at national and local levels from organizations can enhance policy and partnerships that prioritize ocean conservation and protect the integrity of ocean biodiversity.
4. Promoting Sustainable Fisheries and Coastal Management
Sustainable fisheries management is a fundamental piece of the ocean conservation puzzle, ensuring fishing practices do not degrade coral habitats. Implementing fishing regulations, including limits on catch sizes and areas to avoid during spawning, enables fish populations, especially reef fish, to flourish. Proper management of coastal environments, paired with regulations pertaining to coral mining and sedimentation, lessens human-induced stressors that jeopardize coral anatomy and overall reef health.
Integrating Local Fishing Practices
Incorporating traditional fishing practices into modern management strategies can help maintain the ecological balance of coastal waters. Collaborative efforts with local fishers to establish harvesting seasons can increase public awareness and support marine resource sustainability. Additionally, imposing restrictions on harmful methods, such as blast fishing, results in healthier ecosystems and supports local economies resilient to external shocks.
Utilizing Technology for Sustainable Practices
Advancements in technology can enhance sustainable fisheries. Utilizing drone technology for underwater surveying or mobile apps for reporting illegal practices can improve data collection and enhance monitoring efforts of fish populations. By using technology, local fisheries and managers can adopt fisheries management practices based on scientific data, supporting both the economy and coral health.
5. Engaging Citizen Science in Marine Conservation
Risking coral reefs requires collective action; thus, engaging the community through citizen science initiatives is pivotal. Volunteers can participate in reef monitoring programs or educational initiatives that advocate for reef ecosystems management. Citizen science not only aids in data collection but also sparks a personal connection to the oceans, motivating individuals to contribute actively to marine conservation strategies.
Innovative Uses of Technology in Citizen Science
Digital platforms enable amateur naturalists to report sightings of marine species, track coral bleaching events, and provide valuable insights on reef conditions. Examples like the Coral Triangle Initiative and iNaturalist foster active participation from aspiring marine biologists while producing critical data on coral ecosystem health. By raising awareness and educating participants about the significance of coral ecosystems, citizen science initiatives build a solid foundation for effective marine conservation.
Collaboration with Conservation Organizations
Working alongside established conservation organizations enhances the collaboration potential of citizen science endeavors. Groups may include NGO-led initiatives focusing on habitat restoration or scientific expeditions that engage volunteers for ongoing research. By partnering with these entities, individuals deepen their understanding of coral ecology while positively impacting coral conservation efforts globally.
Key Takeaways
- Protecting coral reefs requires a multilateral approach, including strengthening marine protected areas.
- Effective coral restoration practices are essential in reviving degraded reef ecosystems.
- Climate action plays a significant role in combating coral bleaching and safeguarding coral health.
- Promoting sustainable fisheries ensures the preservation of coral habitats from overfishing and pollution.
- Engaging citizen science fosters community involvement in marine conservation initiatives.
FAQ
1. What are the main causes of coral bleaching?
Coral bleaching primarily results from elevated ocean temperatures linked to climate change, causing stressed corals to expel symbiotic algae, leading to loss of color and critical nutrients. Other factors such as increased ocean acidification and pollution also exacerbate this phenomenon, making reefs vulnerable to disease.
2. How can marine tourism contribute to coral conservation?
Marine tourism can promote reef tourism that focuses on sustainable practices, educating visitors about coral ecosystems while providing funding for conservation efforts. Well-managed marine tourism enables local communities to thrive while fostering a deep appreciation of vulnerable marine habitats.
3. What role do seagrass meadows play in coral health?
Seagrass meadows are vital for maintaining the health of coral reefs as they provide shelter for juvenile marine life, stabilize sediments, and improve water quality. Sustainable management practices can lead to healthier marine ecosystems, increasing overall biodiversity.
4. How can individuals help protect coral reefs?
Individuals can contribute by supporting sustainable seafood choices, participating in beach cleanups, engaging in marine conservation education efforts, or volunteering for local research initiatives related to coral health. Every small action contributes significantly to the preservation of coral reefs.
5. Why is restoring coral ecosystems important for biodiversity?
Restoring coral ecosystems is crucial to enhancing overall biodiversity as healthy reefs serve as habitats for countless marine species, supporting their survival and allowing for a more balanced oceanic ecosystem. Greater biodiversity fosters greater ecological resilience against environmental shifts.
“`